Cross-section of Titanium AM body with floating guide retained by EB welded ring Macro section of EB weld between AM Ti body and Turned ring from stock bar EB Welding and Additive Manufacturing (AM)/3D Printing Component parts, AM Ti Body, floating guide ring and retaining collar AM can be used to create unique design features in high-strength materials impossible with legacy methods. The AM process for complex parts is slow

Components for aero-engine application machined from billet, running “lights-out” on 5-axis mill 50% reduction in cost through EBP DMF exercise. Machined from Alloy 718 billet including 1.5 mm “O” ring track Demand for products made from hard and tough materials has resulted in EBP developing machining expertise for a range of difficult metals. Current production includes Nickel based alloys 718, C263 & 625, Titanium 6Al-4V, Haynes and Hastelloy. We have
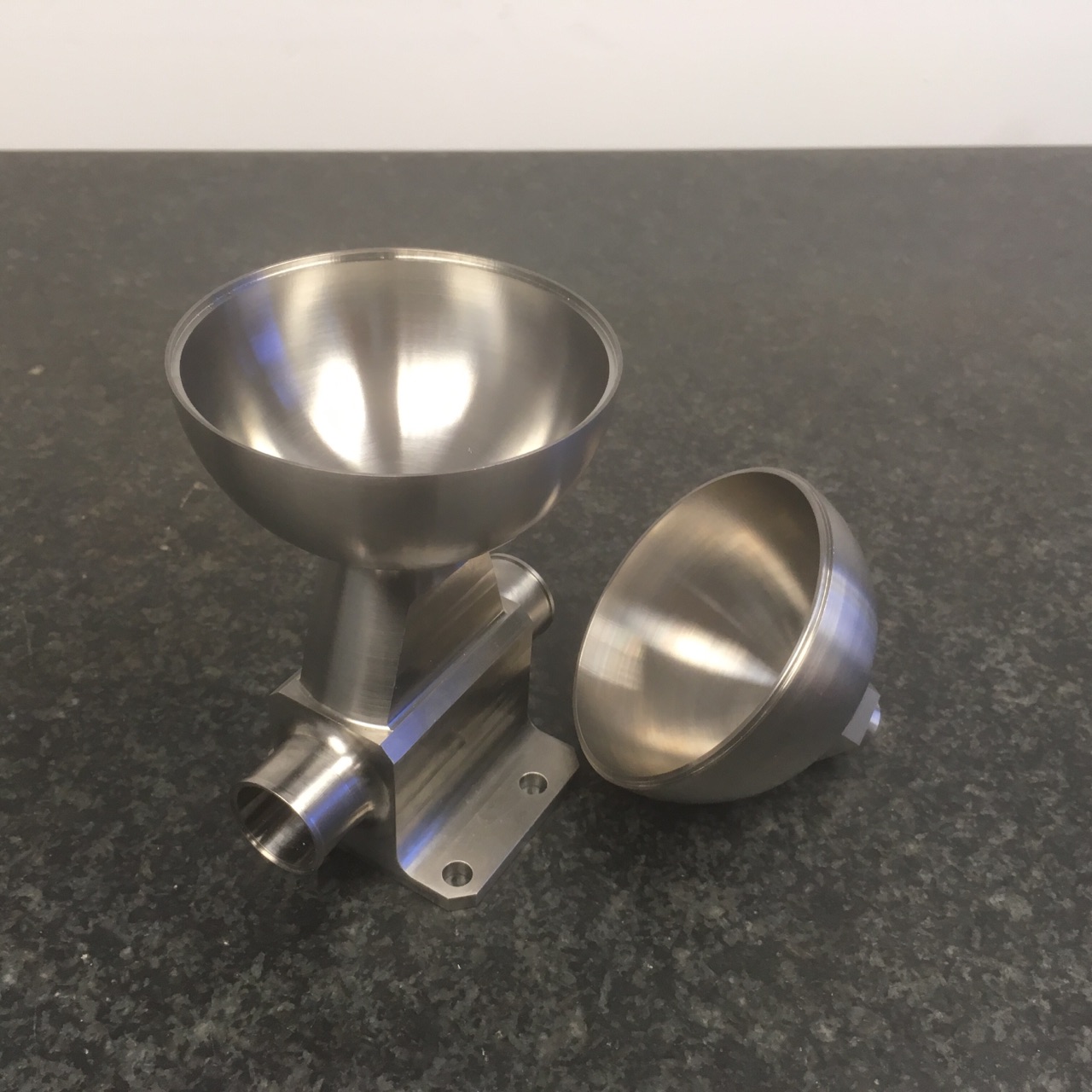

Simple components EB welded as finish assemblies 50% reduction in cost through DFM exercise, machined from Alloy718 billet Design for Manufacturing (DFM) is the process of designing parts, components or products for ease of manufacturing with an end goal of making a better product at a lower cost. This is done by simplifying, optimizing, and refining the product design. We work WITH you not FOR you. With over 50% of

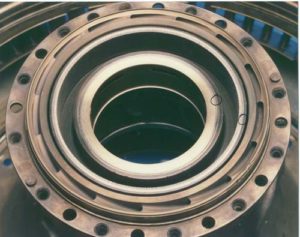
The exceptionally low distortion of EB welding makes it possible to repair or modify high-precision and critcal parts. Examples include; Replacement bearings and seals in Aero-engine casings Modification of finished machined part Repair and recovery of machining errors through EBW replacement material
Electron beam welding is a vital art in many core industries. These include aerospace, oil and gas, and medical equipment. EB welding was invented in the 1950s, which was a time when fusion was very much in vogue. However, electron beams have stood the test of time in terms of their real-world applications. Being able to tightly control electron beams via the combination of a vacuum and precision calculations gives

The electron beam welding (EBW) process is a method of melting metals together to form a joint. A powerful and highly accurate beam of electrons is fired at the joint, causing the material to melt and then re-solidify to create the weld zone. If there is one word that comes to mind when EB welding is mentioned, it’s vacuum. There are three main reasons that a vacuum is used. 1)
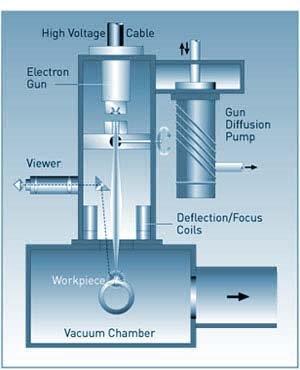
A focussed beam of electrons creates an energy intensity x 1000 greater than Arc welding Which Industries Rely Upon Electron Beam Welding? EBW uses electrons formed into a finely-focused beam with enough power density to melt metals instantaneously. The weld takes place in a vacuum, is normally be achieved without filler and in a single pass, and with minimal metallurgical disturbance. EBW remelts parent material in a vacuum, resulting

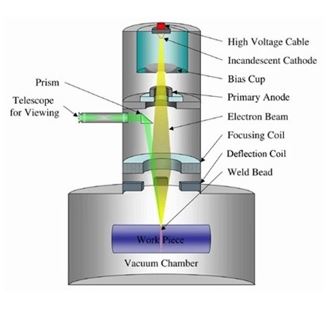
Put very simply, electron beam welding (EBW) is a process whereby two metals are fused or welded together using a beam of high-velocity electrons. This type of welding is suited to applications requiring high-precision, very good repeatability and high-strength. Electron beam welding is carried out in a vacuum atmosphere to ensure that the beam of electrons are consistently in a stable condition and thus preventing any dispersion before they reach
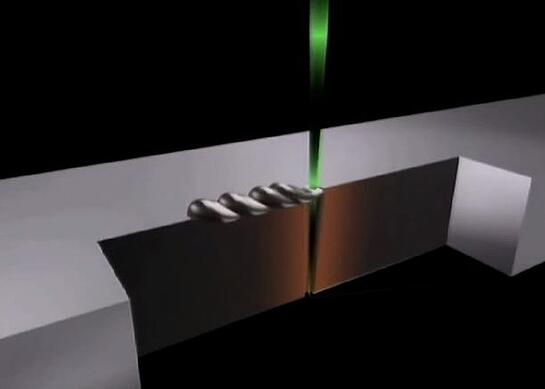
Electron beam welding (EBW) is a metal welding technique which takes place in a vacuum chamber using a beam of high energy electrons to heat the metal. This melts the material, creating a ‘keyhole’ which then solidifies as it fuses with another component. EBW is known for its precision, making it a popular choice for the Aerospace, Defence, Medical equipment and Medical Implant manufacturers, the Motorsport Industry, Nuclear industry, Oil-and-gas

One of the distinguishing features of EB welding is that it requires a vacuum to be successful. Why is this? 1) Prevents Beam Dissipation The Electron Beam is a focused stream of electrons of tiny mass but travelling at incredible speed. When a supercharged electron collides with a comparatively huge oxygen or nitrogen atom in the air, it careers off at an angle. This scatters and dissipates the beam deflecting